Expert Techniques for Drying Grain with Ambient Air
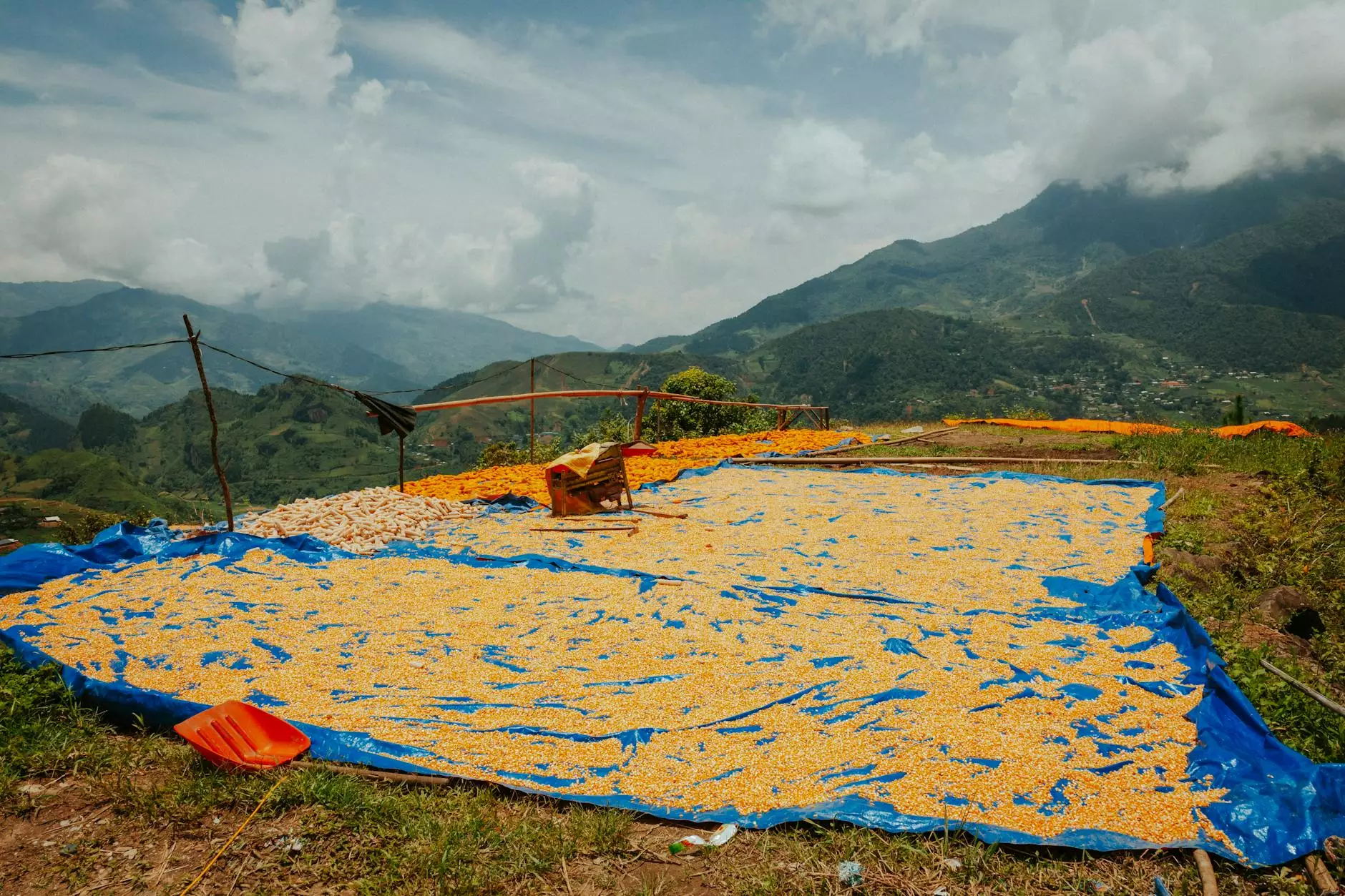

Drying grain with ambient air is an essential practice that every farmer should consider to maintain the quality of their harvest. As agricultural technology advances, understanding traditional and modern drying techniques is crucial for efficient grain management. Let's delve deeper into the methods, benefits, and practical tips for effectively drying your grain using the natural ambient air.
The Importance of Drying Grain
Drying grain is a critical step in the post-harvest process. It prevents spoilage, reduces storage losses, and ensures that the grain meets market quality standards. If left undried, grain can experience various issues, including:
- Mold Growth: High moisture levels provide an ideal environment for mold, leading to crop wastage.
- Insect Infestation: Moist grain attracts pests that can damage stored produce.
- Decreased Market Value: Grain that is not sufficiently dried can fetch lower prices in the market.
Understanding Ambient Air Drying
Ambient air drying involves utilizing the natural air available in the environment to lower the moisture content of grain. This method is particularly beneficial because it requires minimal energy input and is environmentally friendly. Here’s how it works:
1. Basic Principles
Ambient air drying exploits the difference between the moisture content of the grain and the surrounding air. When humid grain is exposed to drier air, moisture will transfer from the grain to the air until equilibrium is reached. This process is influenced by:
- Temperature: Warmer air can hold more moisture, thus accelerating the drying process.
- Humidity: Lower humidity levels in the ambient air will facilitate faster moisture evaporation.
- Airflow: Adequate airflow is necessary to carry away the evaporated moisture and bring in drier air.
2. Equipment Needed
While drying grain with ambient air doesn't require complex machinery, having the right equipment can significantly enhance the process. Essential tools include:
- Grain Aeration Systems: Fans and ducts can help circulate air and create a more effective drying environment.
- Moisture Meters: These devices help monitor the moisture content of the grain and ensure it reaches optimal levels.
- Temperature Sensors: Keeping track of temperature helps in adjusting airflow and managing drying cycles.
Optimal Conditions for Drying Grain
To effectively dry grain using ambient air, certain conditions need to be optimal:
1. Ideal Environmental Conditions
The best time to implement ambient air drying is during the cooler, drier parts of the day or season. Early mornings or late afternoons during fall often provide optimal conditions for drying.
2. Adjusting Airflow
Airflow is crucial in ambient air drying. The airflow should be adjusted based on the ambient humidity and temperature. High airflow rates can accelerate drying but may also cause cooling of the grain if not managed properly.
3. Regular Monitoring
Regularly monitoring moisture levels is essential. Aim to bring the moisture content down to a safe level, typically between 13-15% for most grains. Using a moisture meter will provide accurate readings to guide your actions.
Benefits of Drying Grain with Ambient Air
The benefits of drying grain with ambient air are numerous, making it an attractive option for farmers:
- Cost-efficiency: Reduces energy costs as it relies on natural air, which is a sustainable option.
- Quality Preservation: Helps maintain grain integrity without exposing it to high temperatures that may lead to nutrient loss.
- Environmental Friendly: Minimizes carbon footprint as it reduces reliance on fossil fuel-based drying systems.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drying Grain with Ambient Air
Here’s a detailed guide to successfully implement ambient air drying for your grain:
Step 1: Preparation
Before commencing the drying process, ensure that:
- The grain is clean and free from debris.
- Storage facilities are prepared and sanitized to prevent contamination.
- The drying area is strategically placed to maximize exposure to ambient air.
Step 2: Setting up Aeration
Set up your grain aeration system. This could involve unfolding ducts or pugging the grain correctly in a bin to enhance air movement. Ensuring a well-designed system is critical for success.
Step 3: Monitoring
Keep a close eye on both moisture levels and weather conditions. Utilize moisture meters and temperature sensors during the grain drying to make appropriate adjustments as needed.
Step 4: Storage Post-Drying
Once the grain reaches the desired moisture content, store it in a cool, dry place. This step is crucial to ensure that no further moisture is absorbed from the environment, which can lead to spoilage.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Drying grain with ambient air is beneficial, but it also presents certain challenges:
1. High Humidity Levels
If the ambient humidity is too high, it can significantly slow down the drying process. Consider using dehumidifiers or adjusting your drying strategy to coincide with drier periods.
2. Monitoring Consistency
Inconsistent monitoring can lead to poor drying results. Implement regular checks on moisture levels and adjust airflow accordingly.
3. Weather Dependence
Ambient air drying is reliant on favorable weather conditions. Be prepared with alternative drying methods for unexpected weather changes.
Conclusion
In summary, drying grain with ambient air is an effective, cost-efficient method for maintaining grain quality post-harvest. By understanding the fundamentals of ambient air drying and implementing best practices, you can significantly improve the storage and preservation of your grain products. For reliable farming equipment repair and services, consider visiting tsgcinc.com and discover how TSGC Inc. can support your farming operations.